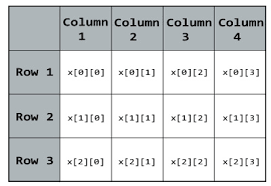
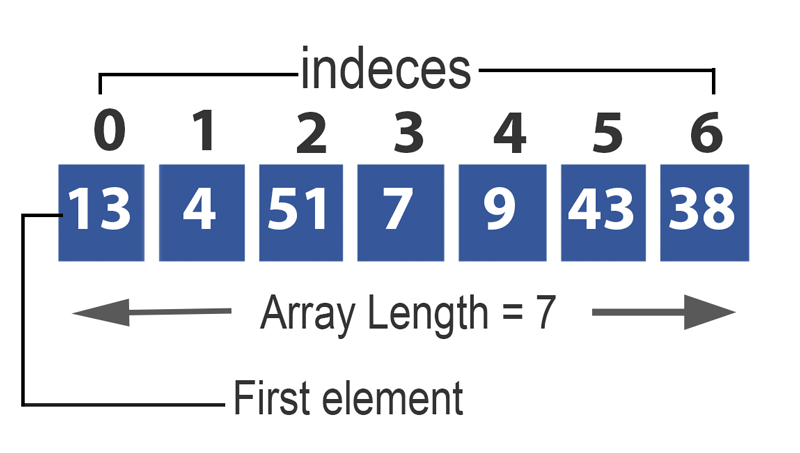
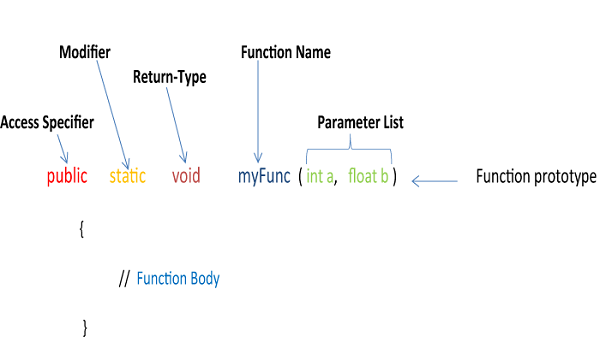
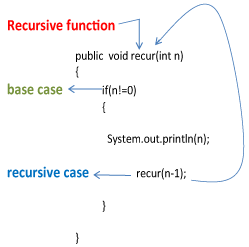
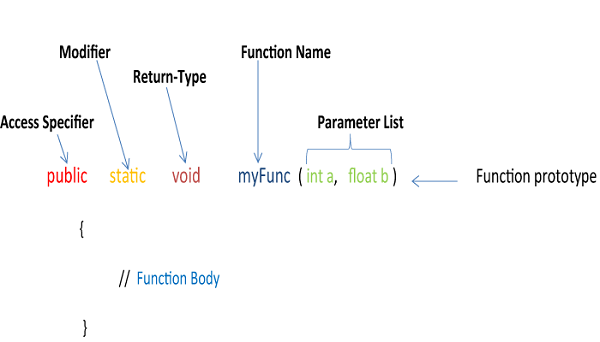
Constructors in Java

CONSTRUCTORS
Constructor is a member function with the same name as that of a class and is used to initialize the data members of the class with a legal initial value.
There are two types of constructors:
- Parameterized constructor – Constructor which receives parameters.
- Non-parameterized constructor (default constructor) – Constructor which does not receive any parameter.
Difference Between Constructor and Method
| Constructor | Method |
|---|---|
| Same name as that of class | Any name (legal identifier) except class name |
| Has no return value | May or may not have a return value |
| Called automatically when an object of the class is created | Called explicitly |
Constructor Overloading
Several constructors in a class that are differentiated by the number or type of parameters they receive are called overloaded constructors and the concept used to create them is called constructor overloading.
Access Specifiers
- Private access specifier refers to the data members/methods that are private to a class and therefore cannot be used outside the class definition.
- Protected access specifier refers to the data members/methods that can be used within the same class as well as in those classes that are derived from it within the same package.
- Public access specifier refers to the data members/methods that can be used in the same class as well as all other classes.
- If no other access specifier is used, the class member takes default friendly or package access which means that data members/methods are accessible within the same class, within the same package but not in the subclasses (derived classes).