Double Dimension Array in Java
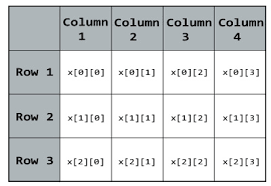
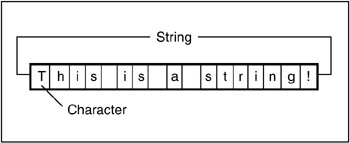
A 2-D array or double dimension array is a continuous location in memory where elements of the same type (datatype) are stored. A 2-D array consists of rows and columns where an element is stored at the cross-section of row and column known as a location. A location is accessed with the help of indeces of rows and columns as shown in the figure below.

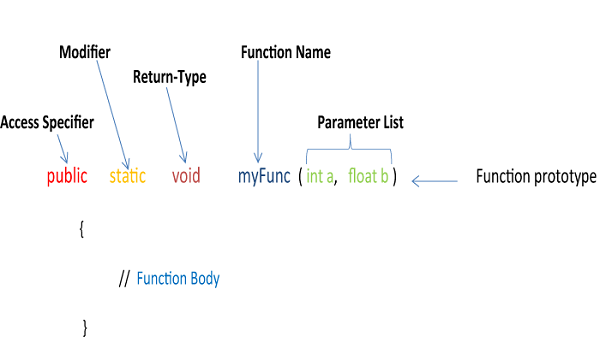
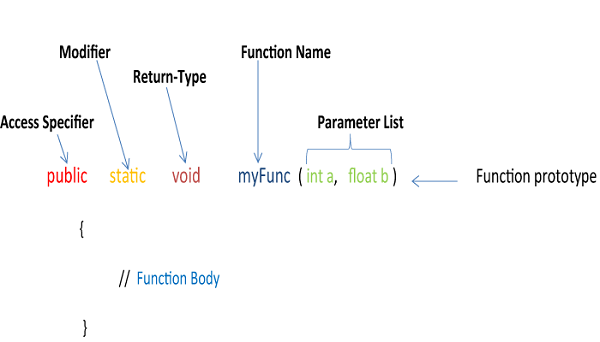
To use an array in a program, you must declare an array first, then assign values to it, and then access it within a loop.
Array Declaration
To declare an integer array:
int a[][] = new int[4][4];To declare a String array:
String a[][] = new String[5][45];To assign values to an array:
System.out.println("Enter "+(4*4)+" integer values");
try{ for(i = 0; i < 4; i++){ for(j = 0; j < 4; j++){ a[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); } } }catch(Exception e){}Accessing array elements
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++){ for(j = 0; j < 4; j++){ System.out.println(a[i][j]); } }
Array Initialization
Integer array:
int a[][] = { {1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9} }String array:
String str[][] = { {"Java", "is", "Robust and Secure."}, {"Java", "is", "platform-independent."}, {"Java", "is", "an", "Object-Oriented."} };